Archaic Sequence Hub


What is Archaic Introgression
The sequencing of archaic human genomes, coupled with the availability of genome sequences from diverse present-day human populations, has revealed multiple episodes of gene flow between archaic and modern humans [5-10]. In particular, non-African populations have 1–2% Neanderthal ancestry [5, 6, 10-13], and Melanesians and East Asians have 3% and 0.2% ancestry, respectively, from Denisovans [11, 12, 14, 15]. Beyond genome-wide proportions, a number of studies have attempted to characterize how introgressed archaic DNA is distributed along the genome [1-4, 16-19]. Analysis of maps of archaic introgression has yielded novel insights into human evolution and biology.
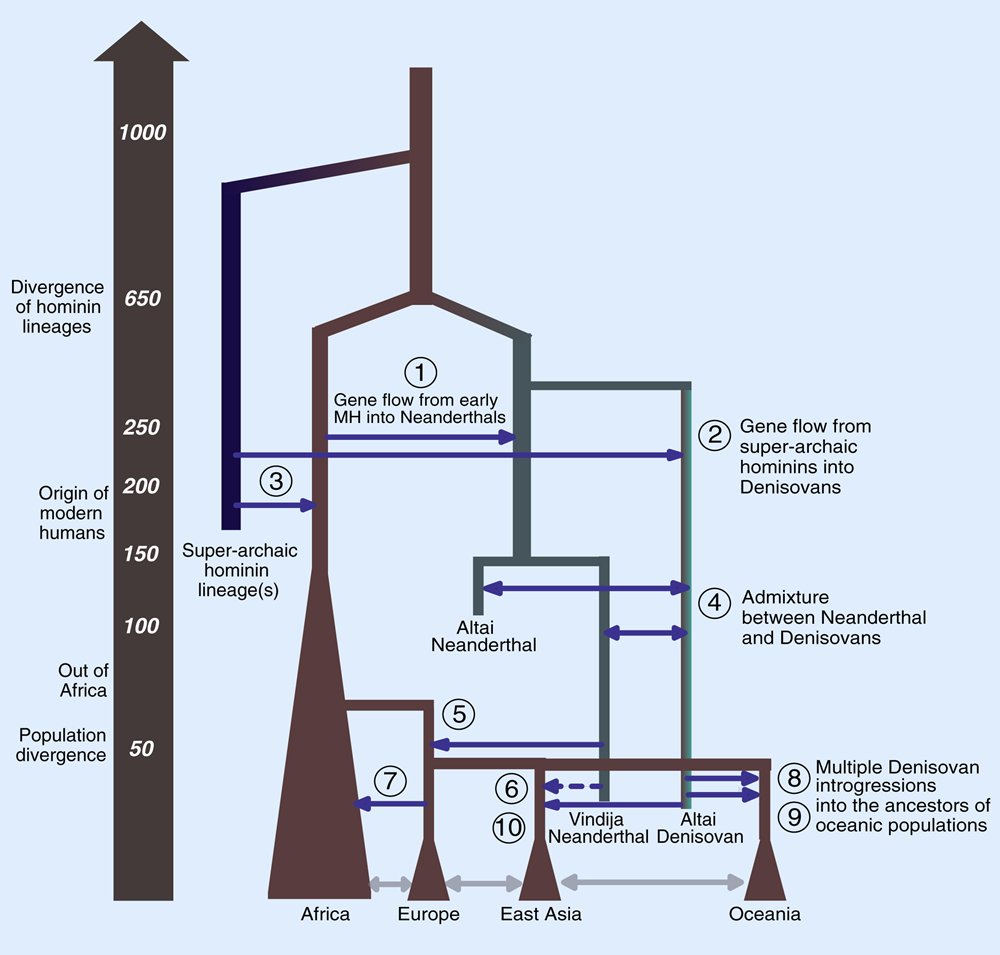
Reilly PF, Tjahjadi A, Miller SL, Akey JM, Tucci S: The contribution of Neanderthal introgression to modern human traits. Curr Biol 2022, 32:R970-R983.

What We Do in This Project
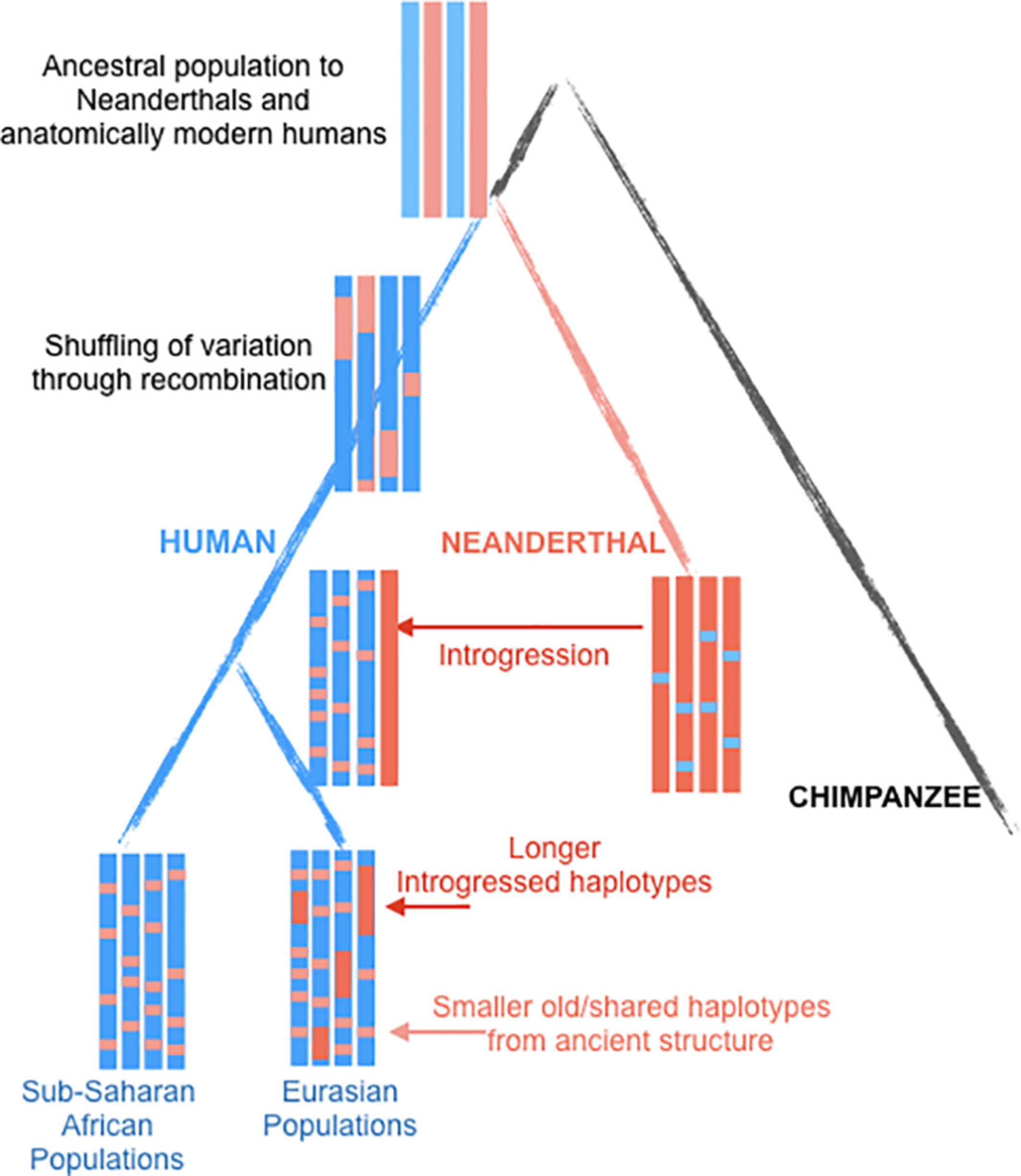
Gokcumen O: Archaic hominin introgression into modern human genomes. American journal of physical anthropology 2020, 171:60-73.
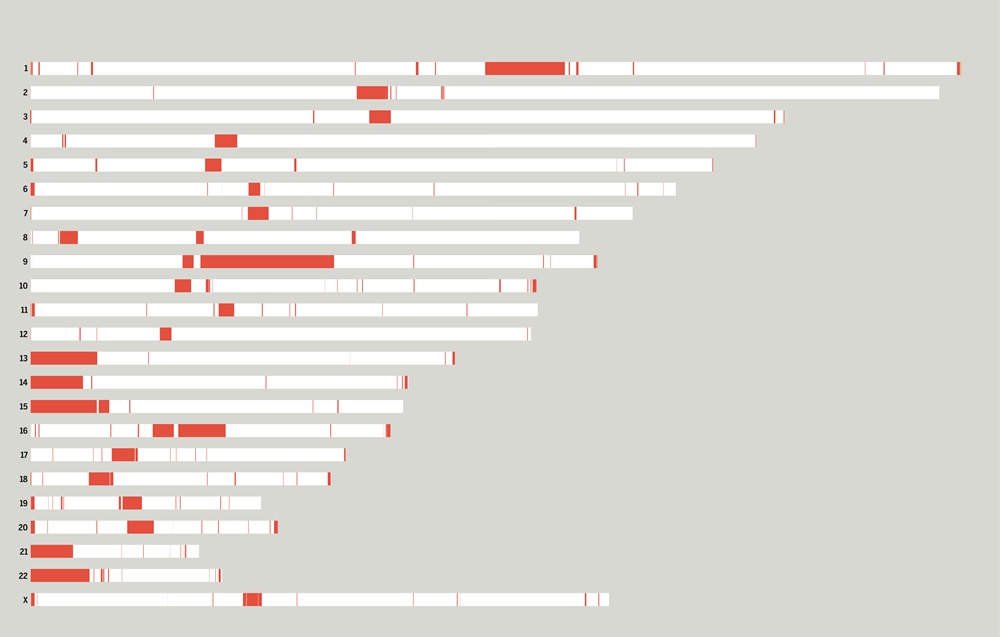
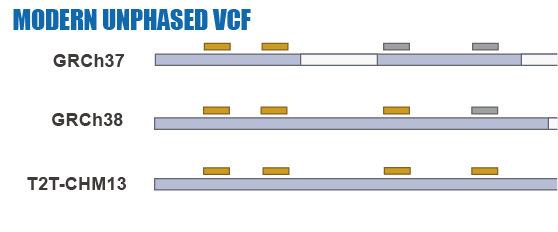
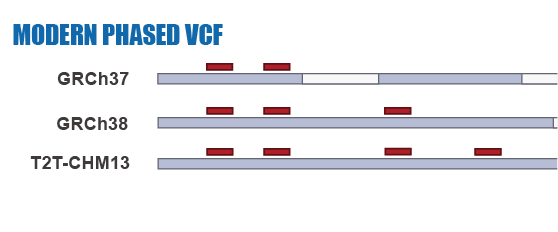
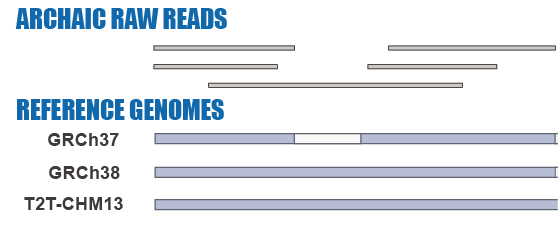
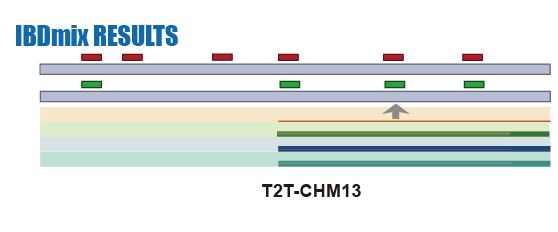
Given the limitations of previous studies, we are currently using IBDmix [16] to detect the archaic introgressed sequences in 2,504 samples from 26 geographically diverse populations in the 1,000 Genomes Project [20], based on the three different human reference genomes. Also, given the absence of publicly available databases specifically focused on archaic introgression in modern humans, we are undertaking this project to integrate the archaic introgressed call sets and their corresponding functional impacts across populations, adding the information to this database. We aim to create a user-friendly, easily accessible, visual platform that enables researchers and/or enthusiasts to browse and explore the information about archaic introgression along the genome according to their specific interests and distinct usage of the reference genomes.
Why a Complete Genome Assembly
Is Essential for Archaic Introgression Analysis
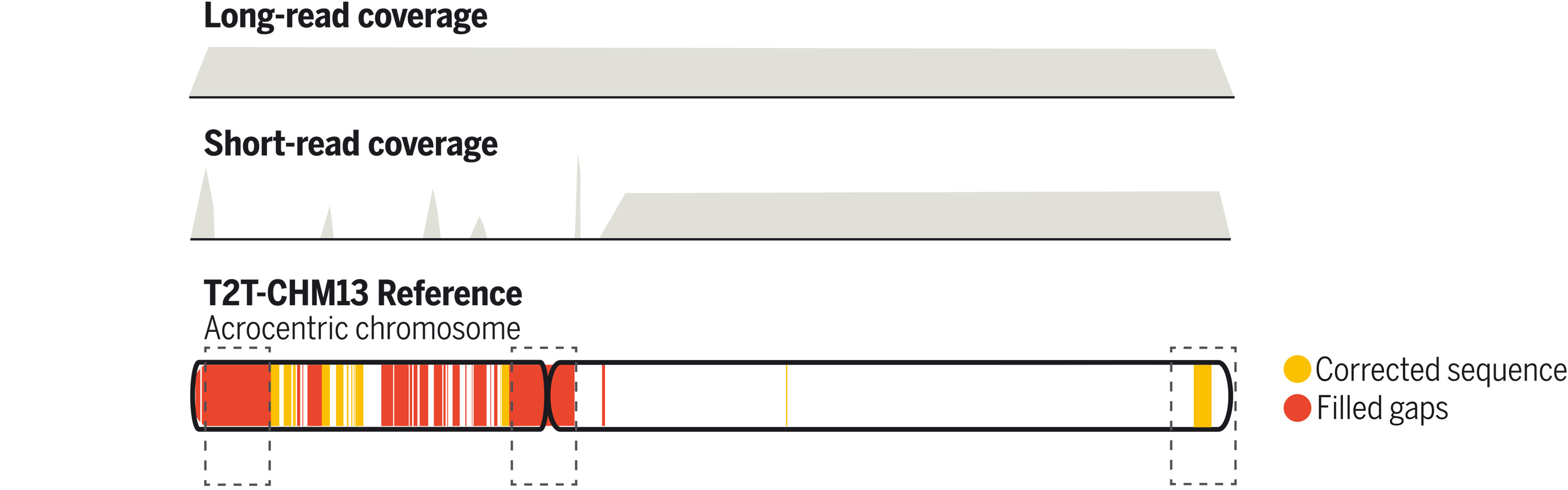
Leveraging long-read sequencing technologies, a complete human reference genome, T2T-CHM13, which corrected errors in prior references and addressed the remaining 8% of the genome, has emerged [22]. The emergence of T2T-CHM13 holds great promise for enhancing our understanding of human genomics, including structures such as segmental duplications, repeats, large-scale genomic differences, and centromeres, which influence epigenomic and population genetics studies [24-28]. Nevertheless, the impact of T2T-CHM13 on introgression patterns in human populations is yet to be elucidated. In light of this, the complete and high-quality human reference genome, T2T-CHM13, provides a unique opportunity to reevaluate and advance our understanding of the archaic genetic legacy left in modern populations.
Nurk S, Koren S, Rhie A, Rautiainen M, Bzikadze AV, Mikheenko A, Vollger MR, Altemose N, Uralsky L, Gershman A, et al: The complete sequence of a human genome. Science 2022, 376:44-53.
Gershman A, Sauria MEG, Guitart X, Vollger MR, Hook PW, Hoyt SJ, Jain M, Shumate A, Razaghi R, Koren S, et al: Epigenetic patterns in a complete human genome. Science 2022, 376:eabj5089.

How we did this
Digging
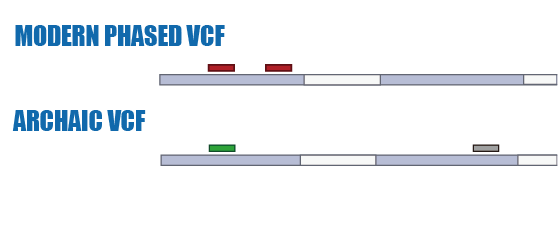
Phasing

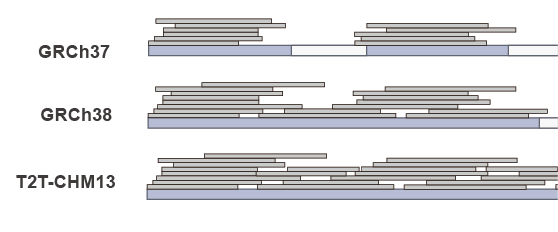
Mapping
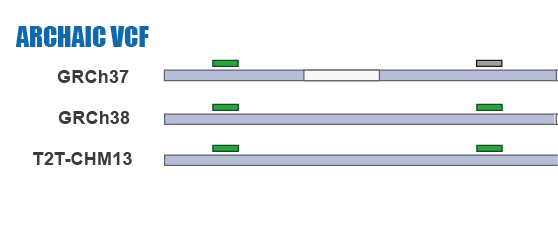
SNP Calling
IBDmix Calling
Function analyzing

What we are working on

Reference
1. Dannemann M, Kelso J: The Contribution of Neanderthals to Phenotypic Variation in Modern Humans. Am J Hum Genet 2017, 101:578-589.
2. Gittelman RM, Schraiber JG, Vernot B, Mikacenic C, Wurfel MM, Akey JM: Archaic Hominin Admixture Facilitated Adaptation to Out-of-Africa Environments. Curr Biol 2016, 26:3375-3382.
3. Racimo F, Gokhman D, Fumagalli M, Ko A, Hansen T, Moltke I, Albrechtsen A, Carmel L, Huerta-Sanchez E, Nielsen R: Archaic Adaptive Introgression in TBX15/WARS2. Mol Biol Evol 2017, 34:509-524.
4. Simonti CN, Vernot B, Bastarache L, Bottinger E, Carrell DS, Chisholm RL, Crosslin DR, Hebbring SJ, Jarvik GP, Kullo IJ, et al: The phenotypic legacy of admixture between modern humans and Neandertals. Science 2016, 351:737-741.
5. Green RE, Krause J, Briggs AW, Maricic T, Stenzel U, Kircher M, Patterson N, Li H, Zhai W, Fritz MH, et al: A draft sequence of the Neandertal genome. Science 2010, 328:710-722.
6. Prufer K, Racimo F, Patterson N, Jay F, Sankararaman S, Sawyer S, Heinze A, Renaud G, Sudmant PH, de Filippo C, et al: The complete genome sequence of a Neanderthal from the Altai Mountains. Nature 2014, 505:43-49.
7. Prufer K, de Filippo C, Grote S, Mafessoni F, Korlevic P, Hajdinjak M, Vernot B, Skov L, Hsieh P, Peyregne S, et al: A high-coverage Neandertal genome from Vindija Cave in Croatia. Science 2017, 358:655-658.
8. Mafessoni F, Grote S, de Filippo C, Slon V, Kolobova KA, Viola B, Markin SV, Chintalapati M, Peyregne S, Skov L, et al: A high-coverage Neandertal genome from Chagyrskaya Cave. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117:15132-15136.
9. Reich D, Green RE, Kircher M, Krause J, Patterson N, Durand EY, Viola B, Briggs AW, Stenzel U, Johnson PL, et al: Genetic history of an archaic hominin group from Denisova Cave in Siberia. Nature 2010, 468:1053-1060.
10. Meyer M, Kircher M, Gansauge MT, Li H, Racimo F, Mallick S, Schraiber JG, Jay F, Prufer K, de Filippo C, et al: A high-coverage genome sequence from an archaic Denisovan individual. Science 2012, 338:222-226.
11. Sankararaman S, Mallick S, Patterson N, Reich D: The Combined Landscape of Denisovan and Neanderthal Ancestry in Present-Day Humans. Curr Biol 2016, 26:1241-1247.
12. Vernot B, Tucci S, Kelso J, Schraiber JG, Wolf AB, Gittelman RM, Dannemann M, Grote S, McCoy RC, Norton H, et al: Excavating Neandertal and Denisovan DNA from the genomes of Melanesian individuals. Science 2016, 352:235-239.
13. Wall JD, Yang MA, Jay F, Kim SK, Durand EY, Stevison LS, Gignoux C, Woerner A, Hammer MF, Slatkin M: Higher Levels of Neanderthal Ancestry in East Asians than in Europeans. Genetics 2013, 194:199-+.
14. Browning SR, Browning BL, Zhou Y, Tucci S, Akey JM: Analysis of Human Sequence Data Reveals Two Pulses of Archaic Denisovan Admixture. Cell 2018, 173:53-61 e59.
15. Mallick S, Li H, Lipson M, Mathieson I, Gymrek M, Racimo F, Zhao M, Chennagiri N, Nordenfelt S, Tandon A, et al: The Simons Genome Diversity Project: 300 genomes from 142 diverse populations. Nature 2016, 538:201-206.
16. Chen L, Wolf AB, Fu W, Li L, Akey JM: Identifying and Interpreting Apparent Neanderthal Ancestry in African Individuals. Cell 2020, 180:677-687 e616.
17. Sankararaman S, Mallick S, Dannemann M, Prufer K, Kelso J, Paabo S, Patterson N, Reich D: The genomic landscape of Neanderthal ancestry in present-day humans. Nature 2014, 507:354-357.
18. Vernot B, Akey JM: Resurrecting surviving Neandertal lineages from modern human genomes. Science 2014, 343:1017-1021.
19. Huerta-Sanchez E, Jin X, Asan, Bianba Z, Peter BM, Vinckenbosch N, Liang Y, Yi X, He M, Somel M, et al: Altitude adaptation in Tibetans caused by introgression of Denisovan-like DNA. Nature 2014, 512:194-197.
20. Byrska-Bishop M, Evani US, Zhao X, Basile AO, Abel HJ, Regier AA, Corvelo A, Clarke WE, Musunuri R, Nagulapalli K, et al: High-coverage whole-genome sequencing of the expanded 1000 Genomes Project cohort including 602 trios. Cell 2022, 185:3426-3440 e3419.
21. Skov L, Hui R, Shchur V, Hobolth A, Scally A, Schierup MH, Durbin R: Detecting archaic introgression using an unadmixed outgroup. PLoS Genet 2018, 14:e1007641.
22. Nurk S, Koren S, Rhie A, Rautiainen M, Bzikadze AV, Mikheenko A, Vollger MR, Altemose N, Uralsky L, Gershman A, et al: The complete sequence of a human genome. Science 2022, 376:44-53.
23. Schneider VA, Graves-Lindsay T, Howe K, Bouk N, Chen HC, Kitts PA, Murphy TD, Pruitt KD, Thibaud-Nissen F, Albracht D, et al: Evaluation of GRCh38 and de novo haploid genome assemblies demonstrates the enduring quality of the reference assembly. Genome Res 2017, 27:849-864.
24. Aganezov S, Yan SM, Soto DC, Kirsche M, Zarate S, Avdeyev P, Taylor DJ, Shafin K, Shumate A, Xiao C, et al: A complete reference genome improves analysis of human genetic variation. Science 2022, 376:eabl3533.
25. Altemose N, Logsdon GA, Bzikadze AV, Sidhwani P, Langley SA, Caldas GV, Hoyt SJ, Uralsky L, Ryabov FD, Shew CJ, et al: Complete genomic and epigenetic maps of human centromeres. Science 2022, 376:eabl4178.
26. Gershman A, Sauria MEG, Guitart X, Vollger MR, Hook PW, Hoyt SJ, Jain M, Shumate A, Razaghi R, Koren S, et al: Epigenetic patterns in a complete human genome. Science 2022, 376:eabj5089.
27. Hoyt SJ, Storer JM, Hartley GA, Grady PGS, Gershman A, de Lima LG, Limouse C, Halabian R, Wojenski L, Rodriguez M, et al: From telomere to telomere: The transcriptional and epigenetic state of human repeat elements. Science 2022, 376:eabk3112.
28. Vollger MR, Guitart X, Dishuck PC, Mercuri L, Harvey WT, Gershman A, Diekhans M, Sulovari A, Munson KM, Lewis AP, et al: Segmental duplications and their variation in a complete human genome. Science 2022, 376:eabj6965.